Digital government
Open Government Data
|
What is Open Government Data? Open Government Data (OGD) is a philosophy- and increasingly a set of policies - that promotes transparency, accountability and value creation by making government data available to all. Public bodies produce and commission huge quantities of data and information. By making their datasets available, public institutions become more transparent and accountable to citizens. By encouraging the use, reuse and free distribution of datasets, governments promote business creation and innovative, citizen-centric services.
OGD can pose some tricky questions for governments, such as who will pay for the collection and processing of public data if it is made freely available? What are the incentives for government bodies to maintain and update their data? And what data sets should be prioritised for release in order to maximise public value? Steps are therefore needed to develop a framework for cost and benefit analysis, to collect data, and to prepare case studies demonstrating the concrete benefits - economic, social, and policy - of opening government data. The OECD Open Government Data project aims to progress international efforts on OGD impact assessment. The mapping of practices across countries will help establish a knowledge base on OGD policies, strategies and initiatives and support the development of a methodology to assess the impact and creation of economic, social and good governance value through OGD initiatives.
The methodology was first put forward in the Working Paper Open Government Data: Towards Empirical Analysis of Open Government Data Initiatives, and is being validated in collaboration with government representatives from OECD countries as well as non-government stakeholders. OECD OGD analysis includes:
Policy & Working Papers
|
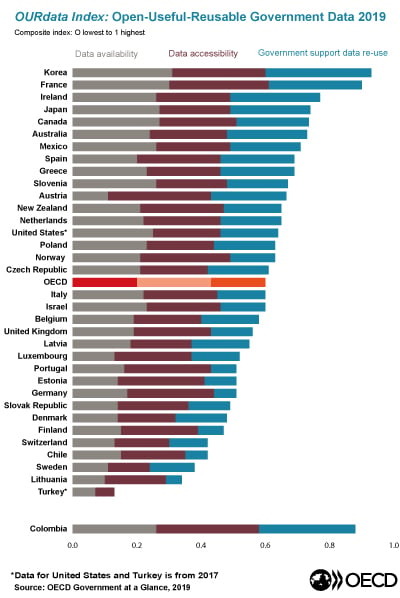
OECD OURdata Index on Open Government Data The OECD OURdata Index assesses governments’ efforts to implement open data in the three critical areas - Openness, Usefulness and Re-usability of government data.
Meetings
Reports |
Related Documents